Optical Lenses

தயாரிப்பு விளக்கம்
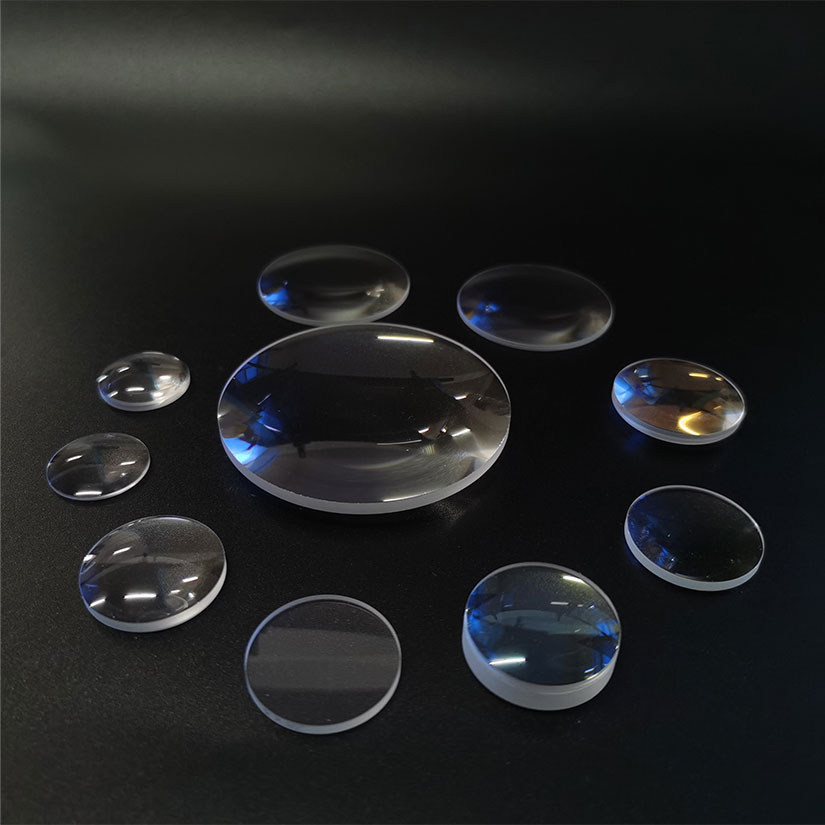
An optical lens is a transparent device made of glass or other transparent materials with the purpose of focusing or diverging light. Lenses play a crucial role in optics and are widely used in various optical instruments such as eyeglasses, cameras, microscopes, telescopes, and binoculars. Selecting the right optical lenses involves considering several factors to ensure they meet your specific vision needs and preferences, like Prescription Requirements, Lens Material, Lens Design, Coatings, etc. This article will introduce you the types of Optical Lenses, it's working principle, materials, application, etc.
Optical Lenses Types and Shapes
Optical lenses come in various types and shapes, each designed to serve specific purposes in different optical applications.
Positive Lenses
Positive lenses, also known as converging lenses, are a type of optical lens that brings parallel rays of light together to a focal point. These lenses are thicker in the center than at the edges. Positive lenses are commonly used in various optical devices and applications.
Characteristics:
Convergence: Positive lenses converge light rays that pass through them. Parallel rays of light are bent towards a common focal point after passing through the lens.
Thicker Center: The center of a positive lens is thicker than the edges. This shape contributes to the converging nature of the lens.
Focal Point: Positive lenses have a real focal point where converging light rays actually meet. The distance from the lens to the focal point is called the focal length.
Magnification: Positive lenses are often associated with magnification, making them useful in magnifying glasses and optical systems.
Negative Lenses
A negative lens, also known as a diverging lens, is an optical lens that causes parallel rays of light to diverge as if they were coming from a virtual focal point. Negative lenses are thinner in the center than at the edges. These lenses have specific features and find applications in various optical systems.
Characteristics:
Divergence: Negative lenses cause parallel rays of light to spread out, creating the illusion of diverging from a virtual focal point.
Thinner Center: Negative lenses are thinner in the center and thicker at the edges.
Virtual Focal Point: Negative lenses create a virtual focal point where the diverging rays appear to originate.
Curvature: The surfaces of negative lenses are curved, with the center being less curved than the edges.
Meniscus Lenses
A meniscus lens is a type of lens with one concave (inwardly curved) surface and one convex (outwardly curved) surface, resembling the shape of a crescent moon or a double-convex lens with one side flattened. This unique design gives the lens distinct features and makes it suitable for various applications.
Characteristics:
Asymmetric Curvature: Meniscus lens has one side that is concave and one side that is convex. The concave side is less curved than the convex side.
Thickness Variation: The lens is thicker at its center and thins out toward the edges.
Reduced Spherical Aberration: The meniscus shape helps reduce spherical aberration, improving image quality.
Focusing and Magnification: Meniscus lenses are used for focusing light in optical systems, contributing to magnification.
Aberration Correction: They are used to correct optical aberrations in certain optical instruments.
Spherical Lenses
Spherical lens is one of the lenses whose surfaces are sections of a sphere. There are two main types of spherical lenses: convex lenses and concave lenses.
Convex Lens
A convex lens is a type of optical lens that is thicker in the center than at the edges. Also known as a converging lens, it converges parallel rays of light to a focal point. Convex lenses have several distinctive features that make them useful in various optical applications.
Characteristics:
Convergence: Convex lenses cause parallel rays of light to converge or come together at a focal point after passing through the lens.